What Is Bitcoin?
We have all heard about Bitcoin, we have seen its logo, and the movements of bitcoin rates are widely discussed in media. It comes into our life, as every day more and more companies start accepting BTC, even in Switzerland and in the state of Arizona, USA is going to allow its citizens to start paying taxes in bitcoins. Still, lots of people wonder: “What is bitcoin?” What does it look like, where are the coins stored, and what does it mean to own and spend them? There are many questions that may seem complicated at first sight, and even scare away newcomers.
We offer you a brief bitcoin guide to shed light on general issues about this revolutionary digital currency — its history, technology, where it comes from, and what are its benefits over regular money.
Table of Contents
BTC Short History
The world first heard of Bitcoin late in the summer of 2008, and on the 31st of October someone named Satoshi Nakamoto published an introduction of the new cryptocurrency. In the article “Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System”, the author told the general idea of the Bitcoin system, the mechanism of transactions, and their verification. He explained how new coins are created and how they are protected from fraud.
In the beginning of 2009, Satoshi Nakamoto published an open-source software of Bitcoin and created the first block, giving life to the blockchain. From the note that was enclosed in that genesis block we know the exact birthday of the first bitcoin — January 3, 2009. Satoshi did not stop on a single coin, he mined about one million of them during the first few months. He sent 10 BTCs to Hal Finney, a cryptographic activist, a developer of the reusable proof-of-work idea. He became the first receiver of bitcoins.
In a little more than a year, Satoshi Nakamoto disengaged himself from any bitcoin management. He gave the keys of the software to Gavin Andresen, who decided to mitigate the dependence of the entire system on one person. His idea was to make it work whatever happens to him or any other individual or company. It was the final step in the decentralization of bitcoin. In 2017, two major changes in the software were accepted, which lead to the creation of Bitcoin Cash and Bitcoin Gold.
Who Can Control Bitcoin?
After the reorganizations that were made by Gavin Andresen, the bitcoin system was no longer controlled by any one person or institution. There are companies like Bitcoin Foundation that work with this cryptocurrency and encourage people all over the world to use it. They may create different applications to operate bitcoins and suggest improvements to the open source code, but they cannot interfere in the protocol or bring changes to previous transactions. No matter what platform or software you use — you have to follow the common rules of buying, spending, and mining bitcoins.
What Is Blockchain?
Blockchain is the instrument that makes the bitcoin system more reliable than banks and governments, which emit and regulate fiat money. That is a big claim, you may say. Well, here are some facts. When we buy and sell something, or transfer the funds from one bank account to another, the deal has to be documented and accounted. This bookkeeping is commonly confidential information. This is why you can trust your bank, but you are never 100% sure that your money is still in your account and you can take it whenever you want. The participants of the trade need the trusted authorities, financial institutions, and accountants to facilitate and validate the deals. Even when you take cash from your customer, you can only assume that the banknote is not counterfeit.
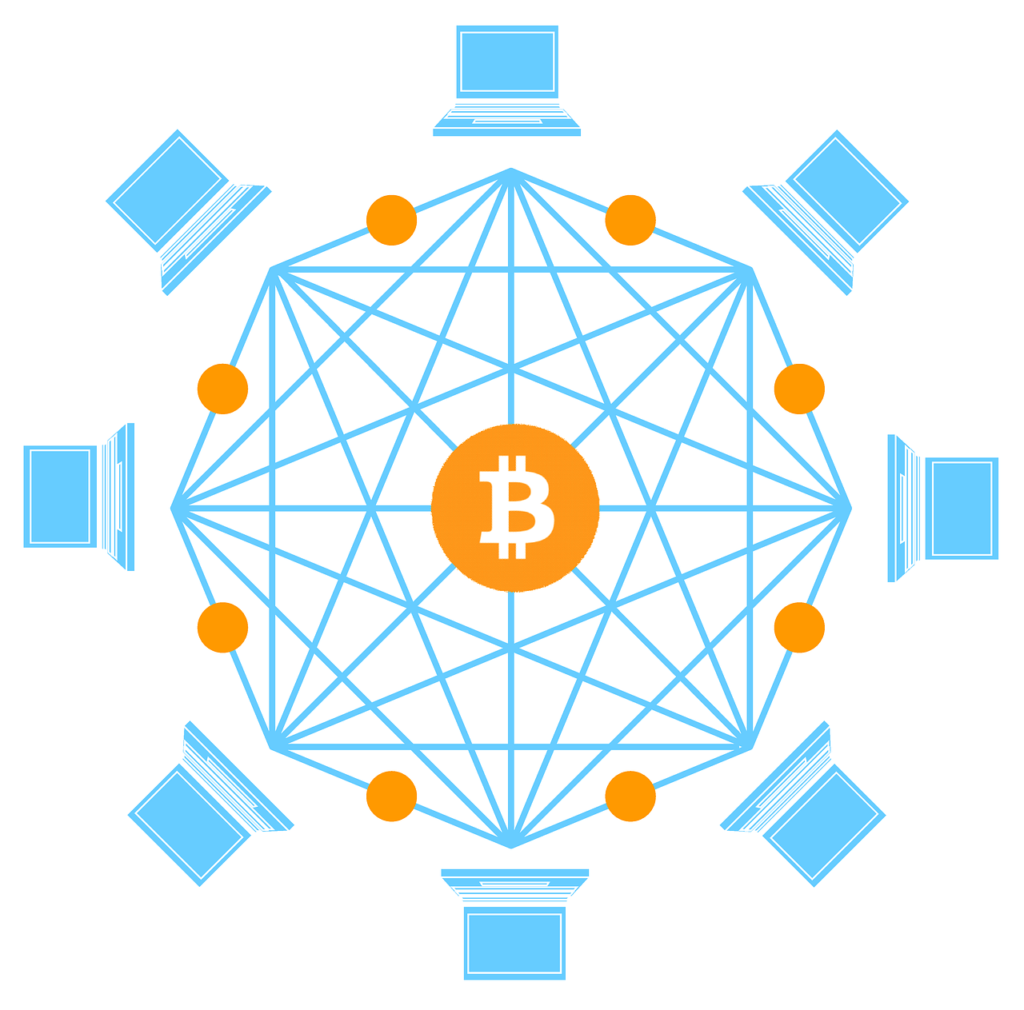
Blockchain is a completely different mechanism of bookkeeping. First of all, you do not need any third trusted party to make records and verify the deals. Once the transaction is made, it is checked and approved by the system, and after this it becomes irreversible. Secondly, all records that have ever been made are transparent. Every user can check when and how many bitcoins were sent from one wallet to another.
The transactions are gathered in the blocks, which are organized in the chain and published on the network. Each new block contains all the information about all previous ones. This way, the system is stable and all attempts to hack it are useless. Summarizing the above, our definition of the blockchain is as follows — it is a public ledger, which is maintained by bitcoin members from their computers via the internet.
Bitcoin Mining and Farming in Simple Words
We mentioned the users who verify the transactions and place them into the public ledger with the help of their computers. Here we have to explain about mining and the people who mine bitcoins. In simple terms, some participants of the bitcoin network employ their computing powers to do some calculations. As a result of their work, when they find the solution to a mathematical task, a new block of confirmed transactions is created and added to the chain. Here we have the first very important role of miners — they verify the transactions and build the blockchain.
The second, but no less important, function is actually to mine new coins. When the new record is placed in the public ledger, the system emits a fixed amount of BTCs and gives them to the miner who completes the task. This is the only way to produce new bitcoins, and their number is limited. For now, the reward is 12.5 BTC per each new block, but in a couple of years it will be cut in half. The term “farming” appeared comparatively recently, when the computing powers of gadgets increased essentially. To get the profit, miners construct bitcoin farms, which are the large data centers with many machines that combine their capacities to deal with the mathematical problems. Farmers have a huge advantage over miners with a single computer, gathering huge harvests and making it into a whole industry.
How Bitcoin Works
We are now at the point where we can tell you how bitcoin works without getting into a complicated technical explanation. Beginners see only a special software that performs as an electronic wallet. You install it on your gadget or sign in to the online version and get your personal BTC address, which can be given in the form of a QR code. It works in the same manner as an email address — you give it to people so they can send you bitcoins. Having the addresses of other users, you can transfer your units to their wallets, too. Seems easy, right?
Yet, we already know that to enable this simple and fast bitcoin trade, miners have to do their work verifying transactions and building a blockchain. A sender of BTCs attaches the unique electronic code to every transaction, which is actually the proof that the units were sent from a particular wallet by its owner personally. This way, every user can be sure that no one can send the same bitcoins twice or thrice, or cancel the deal after it is confirmed by a miner and documented in the ledger. As soon as I give you my bitcoin — it is yours, as if it was something material.
Bitcoins Benefits
Getting started with bitcoins, you will be interested to know about the benefits of this payment system. There must be a reason why so many people want to have bitcoins, and why business leaders all around the world begin to accept BTCs. Fiat money has existed since the beginning of the human civilization and seems to do its work well. There are many online payment solutions that also work on the internet. They were established long before the invention of the cryptocurrencies, so why bitcoin is so attractive? Here are the main advantages of digital money over traditional currencies.
Decentralized
You may remember that Bitcoin does not have any central authority or individual who controls it. To understand how important it is for the bitcoin system, you need to read the white paper by Satoshi Nakamoto, where he introduced his cryptocurrency. Two first parts of it, “Abstract” and “Introduction”, are entirely about the decentralization of BTC. The author underscores the main problem of electronic payments — they all have to be under complete control of the financial institutions to avoid double spending. It causes lots of problems:
- it is necessary to disclose the personal information;
- it is almost impossible to make all transactions irreversible;
- the transaction fees are higher;
- high risk of fraud.
Satoshi Nakamoto suggests getting rid of the trusted third parties and creating a peer-to-peer network where all transactions are facilitated and confirmed by bitcoin users. He offers using mathematics to prove the deals and build the unalterable chain of records. It makes Bitcoin attractive to those who want to trade without interference from the banks’ governments, as two participants can send bitcoins directly to each other. While bitcoin users maintain the ledger and they are economically motivated to keep it working flawlessly, fraud is simply profitless.
In order to change the chain, the attacker or a group of hackers need more computing capacities than all honest bitcoin nodes together. Another big advantage of Bitcoin decentralization is that it is not exposed to the risks of artificial devaluation, economic downfalls, and geopolitical crises.
Fast
In many situations, bitcoin works faster than traditional money. For instance, it takes a couple of minutes to register an online BTC wallet. Compare it with going to a bank and opening an account there. With your public key (another name for BTC address), anyone can put the coins in your wallet quickly and directly; they even do not need to leave their comfortable armchair. The same works with you, as transferring bitcoins to another wallet takes one or two mouse clicks.
Bitcoins can work a lot better than the usual currencies for international shopping. Each electronic transfer of usual money involves an intermediary to check and validate the deal. The problem is the same — no one should be able to spend the same money twice or thrice. Sometimes, the intermediary is a mint that takes payment units from the sender, checks if everything is correct with the deal, and then issues new units to pass them to a receiver. Thus, the system guarantees that coins, which come from the trusted mint, are valid. It is easy to imagine how much time this process takes. All the more, those intermediaries take huge commissions for their services and make you identify yourself.
The Bitcoin creator wanted to make it work faster and he succeeded. We do not need the third parties and mints anymore, as bitcoins go directly from one wallet to another and the time of verification does not depend on state borders, national laws, and instructions. It means that the purchase can be confirmed as soon as 10 minutes after you send the BTCs.
Anonymous
Concerning identification, there is one very popular question. Is bitcoin anonymous? On the one hand, the public ledger is open and the information about all transfers is disclosed. What kind of confidentiality is this, you may ask, when anyone willing can look inside my wallet and see who gives me money and how I spend it. On the other hand, your wallet does not contain any information about you — neither your personal information nor your bank accounts. Yes, escrows and exchanges may require a certain know-your-customer level, but often it is only verification via email. Anyway, blockchain itself does not know your name, physical address, date of birth, age, and gender.
Easy
As we have already said, for an ordinary user Bitcoin is just an application. It may work on your computer, mobile device, or website. To register, there is no need to go to some office, wait in lines, and fill out dozens of papers. You can buy and sell bitcoins, do shopping online, or play the market easily right from your PC. Mobile apps can scan QR codes, so you can pay in restaurants, hotels, car wash facilities, or wherever you want with just your smartphone. Bitcoin payments, especially cross-border ones, are easy and even profitable, as they do not fall under any tax jurisdiction and are not controlled by any state.
Another possibility enabled by Bitcoin is sending microtransactions. Bitcoin has its “cents,” which are called satoshis, after Satoshi Nakamoto. One satoshi equals 0.00000001 BTC. It is the smallest unit that can be sent, and at current rates it costs less than one hundredth of a penny.
Transparent
Transparency of the blockchain is one of the most essential characteristics of Bitcoin. Let’s assume that you are going to receive some bitcoins from another person. Theoretically, you can trace the entire chain of transactions and see if the sender possesses the necessary amount. At the same time, transparency can play a bad joke on BTC owners. When someone uses the same public key for all transactions, his or her entire bitcoin history is known to all participants. It is highly likely that one of the bitcoin members knows you personally.
Thus, this person can see into your pocket and peep at your financial operations. Furthermore, if you buy bitcoins at exchanges, you may be forced to register with your real name, address, and even credit card data. This is why one common advice for BTC users is to create a different address for each operation.
Non-Repudiable
It was briefly mentioned above that BTC transactions are irreversible. This benefit is worth a detailed explanation for understanding bitcoin better. Units can be sent from one user to another, and this process can easily be compared with passing something from hand to hand. If you give a banknote to someone, and he or she puts it in a wallet — you cannot cancel it or withdraw your money back. You can ask the new owner to give it back to you, yes, but it is not the same as a repudiation. This is the centerpiece of the whole idea — Bitcoin is based on a common consensus of users that after the transaction is confirmed, no one can change or withdraw it. It was realized in the Bitcoin protocol to make the blockchain stable and unalterable. This way, when a new BTC member joins the network, he or she agrees that the current state of the public ledger is correct.
What Is the Future of Bitcoin?
The future of Bitcoin, as the future in general, is unknown. It is useless to predict anything, but still we can see the statistics and trends, analyze this information, and plan our own operations. For now, bitcoin seems to remain very attractive for traders, companies, and ordinary users. People and businesses choose it because it lets them trade safely, anonymously, and quickly, without the burden of red tape, taxes, and fees.
Yes, the situation is changing with time, and many countries, like the USA, Switzerland, China, Japan, etc., are trying to develop their laws to take control over cryptocurrencies, including bitcoins. It is quite likely that soon they will find a way to make bitcoin users pay taxes and to regulate all operations with BTC. What will happen then? Will bitcoin still exist after it loses its main distinguishing characteristics, or will it decrease in value and disappear? It has happened before with other currencies, and it can happen again. For now, bitcoin preserves its benefits over fiat money:
- stays decentralized and independent;
- keeps the users’ information confidential;
- adheres to the principle of transparency and irreversibility;
- makes the life of its users easier and more comfortable.
As long as it stays on these positions, it will be in demand.
FAQ
Of course, we cannot tell you all about Bitcoin in this article. We have analyzed the common questions asked by newcomers and decided to answer them herein. Usually, beginners are interested in basic and practical information. We hope the following FAQ paragraphs will be useful for our visitors.
Who Is Bitcoin Creator?
Satoshi Nakamoto is the name which was on the initial paper, where the author introduced his invention. No one knows if it is the real name of a real person, and no one even knows if bitcoin was created by a single man, woman, or a group of programmers. Anyway, since Bitcoin is not under the control of any person or entity, it is not so important who actually is the creator. He, she, or they have no power to affect the system. Bitcoin theory had predecessors — b-money, created by Wei Dai, and BitGold, the project of Nick Szabo. They both got one of the first bitcoins from Satoshi Nakamoto as a gift.
How Many Bitcoins Exist?
Since all countries have rejected the gold standard, national banks can issue their currencies without any control, which sometimes leads to inflation and devaluation. Bitcoin suggests a solution for this problem — to limit the emission. The maximum amount of bitcoins that the system can ever issue is 21 million. Furthermore, the number of coins that are created as a result of adding new blocks to the blockchain decreases every four years. The next cut is going to happen in the year of 2020. It is supposed that demand should always exceed supply, stimulating the interests of investors and, consequently, the exchange rate. Obviously, we cannot tell you how many bitcoins exist at the moment, as this number changes every ten minutes. However, it is known that by the end of March 2018 there are almost 17 million BTC in circulation.
Is Bitcoin a Ponzi Scheme?
It is useless to ask a developer of a financial fraud about his project, as you will never hear the truth. To understand if Bitcoin is or is not a Ponzi scheme, we need to know the meaning of the latter. This operation pays returns to early investors from the funds, which it receives from later investors. Any Ponzi scheme is doomed to fail when it cannot engage new participants.
Let’s compare it with Bitcoin. First of all, there is no central entity that gets all profits. Secondly, the emitted coins are given to miners as the reward for their work. Bitcoin is not an investment project, as it is commonly used as a comfortable and advantageous payment system. And the last reason why BTC is not a fraudulent scheme — its price is not fixed and changes unpredictably. No one knows when the bitcoin owners can raise or lose their money.
Can I Stay Anonymous While Buying Bitcoin?
Yes, you can. If you buy bitcoins on the platforms where you do not have to reveal your personal information — the seller and the escrow will not have a clue who you are and where you live. Unfortunately for those who prefers privacy, the exchanges that require nothing more than email address confirmation take the biggest commissions.
Why Bitcoin Is Different from Other Cryptocurrencies?
We are aware that bitcoin was the first cryptocurrency, and thus it has lived longer than any other cryptographic money. It is more popular and reputable, the demand for bitcoins on the market is greater than that for any altcoins. Consequently, there are more exchanges, software programs, hardware platforms, and traders that work with BTC. Other cryptocurrencies try to tag along behind bitcoin, following its movements. Bitcoin is more interesting for hackers and attackers. The reason for this is exactly the same — it is a leader of the cryptocurrency market. People also trust it because they are sure that no one owns the ledger and rules the system. As a conclusion, there are two main characteristics that differentiate bitcoin from other cryptocurrencies:
- it has a higher credibility among users;
- it is truly decentralized.
It can happen, though, that altcoins may become more valuable due to the novelties they introduce in their projects. For example, Zcash offers the highest level of privacy while Dash provides the fastest transactions. Ethereum developed new functions of the blockchain and increased its rates fourfold in 2017.
Bitcoin Hash: What Is It?
We told you about the mathematical task that a miner has to solve in order to mine a new block of transactions and add it to the chain. The problem consists of encoding the entire information of the block into a randomized character sequence, which has to include the data from the current block and from the previous one. This code is a bitcoin hash.
A hash rate is the measure of the difficulty of this task. This rate changes depending on how many miners are doing their work at the moment. Actually, their computers simply try to guess the necessary combination. Anyway, another meaning of the word “hashing” is a mathematical method of making small numbers from larger ones. A computer takes the information from the block and randomly picks characters there to build the combination. If it is wrong — it does it again and again, and the one that finds the right code first is the winner.
Why Bitcoin Is So Volatile?
The high volatility of bitcoins can be explained by their comparatively small total value and the fewer number of users than it can have. It causes significant changes in the price as a result of unimportant and sometimes unnoticeable events on the market, deals, and changes in supply and demand. It is expected, though, that this volatility will reduce with time, when more people use bitcoins and its role in the global economy grows.
BTC Interesting Facts
We hope this article helped you to learn some new information about Bitcoin. We tried to explain the basics of the first cryptocurrency in simple terms, to make it readable but informative. Our site FAQBitcoin contains dozens of interesting articles, reviews, instructions, and guides that can help you get started with BTCs and use them safely, with the maximum profit and comfort.
To finish this paper on a positive note, here are some interesting facts about bitcoins:
- guess who holds the biggest bitcoin wallet? Right, the FBI! They closed the darknet marketplace Silk Road and confiscated the coins. Now the feds own BTCs for 120 million dollars;
- the first bitcoin purchase was a pizza for 25 USD. It happened in 2009, BTCs were worthless then and a buyer gave 10000 coins for his snack. That lucky pizza maker, he must be a millionaire now;
- bitcoin is not tied with the state borders, but it is also an extraterrestrial currency. In 2016, a BTC paper wallet was sent to space, and when it achieved the height of 34 kilometers, people from earth transferred some units on that wallet;
- remember: you should never lose your bitcoin wallet and the private keys of it. Usually, it means that the coins are lost forever too. There is a man with a very bad luck, he threw away the wallet with seven thousand and five hundred of BTCs! It was calculated that almost a quarter of the total amount of bitcoins was lost.
Read more interesting articles about BTC on FAQBitcoin!